Application Architecture
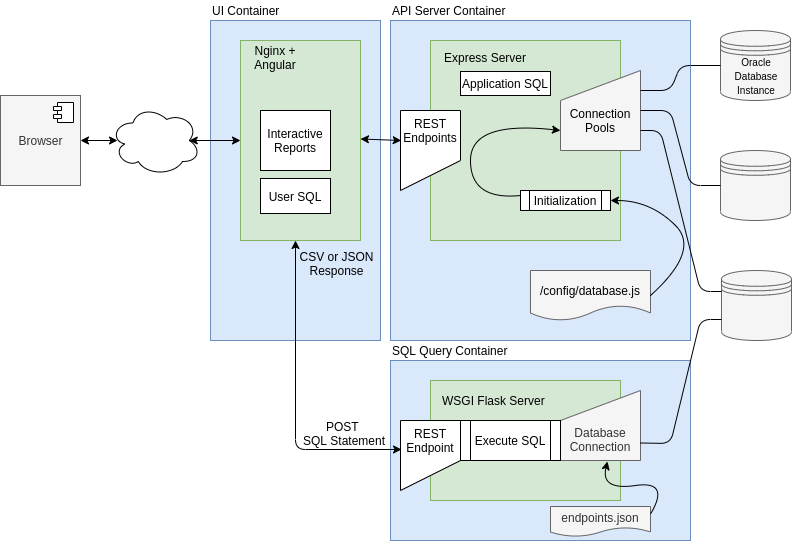
Visulate for Oracle creates 3 docker containers to deliver a browser UI and REST endpoints for one or more Oracle databases. The UI Container exposes an Angular UI which makes API calls to REST endpoints exposed by the API Server Container and the SQL Query Engine Container.
The API Server is an Express JS instance. It connects to one or more registered databases using node-oracledb. Database connections are registered by adding an entry to a configuration file that the API Server reads during initialization. It creates a connection pool for each entry in the config file.
API Server
The API Server has SQL for each database object that queries the appropriate dictionary views (e.g. DBA_TABLES and other views for table objects or DBA_SOURCE for packages). It also queries database’s dependency model to identify dependencies to and from the object (e.g a view “uses” the tables it is based on and is “used by” a procedure that selects from it).
The API Server exposes REST endpoints that allow users initiate queries for a given database + object description. Most API calls include a query against DBA_OBJECTS. For example a call to the /api/{db}/{owner}/{type}/{name}/{status} endpoint returns the result of running the following query in the specified database:
select object_id, object_name, object_type, owner
from dba_objects
where owner = :owner
and object_type like :type
and object_name like :name ESCAPE \_
and status like :status
order by object_name
Results are returned in JSON format. An Open API Specification for the API Server is available in Github.
AI Integration
The API Server can be configured to connect to a Google Gemini LLM. When this feature is enabled Visulate presents a chatbot that can be used for database analysis or code generation. Visulate facilitates this by assembling metadata for use as grounding information by the LLM. This metadata includes details of the current database object and all of its related objects.
UI
An Angular UI makes API calls to the API Server and displays the result.
SQL Query Engine
The SQL Query Engine allows users to run ad-hoc queries and download the result as CSV or JSON. It is a WSGI Flask instance which uses python-oracledb to make database connections. Access to this feature is controlled by a configuration file called endpoints.json. This allows a DBA to limit the list of database environments that allow SQL access. For example, they may wish to allow access for development databases but not production.
The SQL Query Engine exposes a REST API to generate CSV or JSON from user supplied SQL. An HTTP POST request is made to the SQL Query endpoint passing the database credentials as a basic auth header and a SQL query in the request body. A typical request might look like this:
echo -n hr:hr-password| base64
aHI6aHItcGFzc3dvcmQ=
curl \
-L 'https://demo115.visulate.net/sql/vis115' \
-H 'Authorization: Basic aHI6aHItcGFzc3dvcmQ=' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Accept: text/csv' \
-d @- << EOF
{ "sql": "select * from EMPLOYEES where rownum < :maxrows",
"binds": {"maxrows": 10 },
"options": {"download_lobs": "N", "csv_header": "N", "cx_oracle_object": null}
}
EOF
The endpoints.json file populates a Python dictionary of endpoint:connect string pairs. The Query Engine accepts the endpoint as a path parameter (vis115 in the example above) and uses the dictionary to lookup its connect string. It combines this with the username and password passed in the header to establish a database connection. The SQL Query Engine does not use connection pooling. Each request makes a new database connection, executes the query, streams the result and then closes the connection.
Deployment
Visulate for Oracle is deployed as a series of Docker containers on a Google Compute Engine (GCE) virtual machine using Docker Compose. This deployment model provides a balance of performance, ease of management, and scalability for most database documentation and analysis tasks.
Architecture
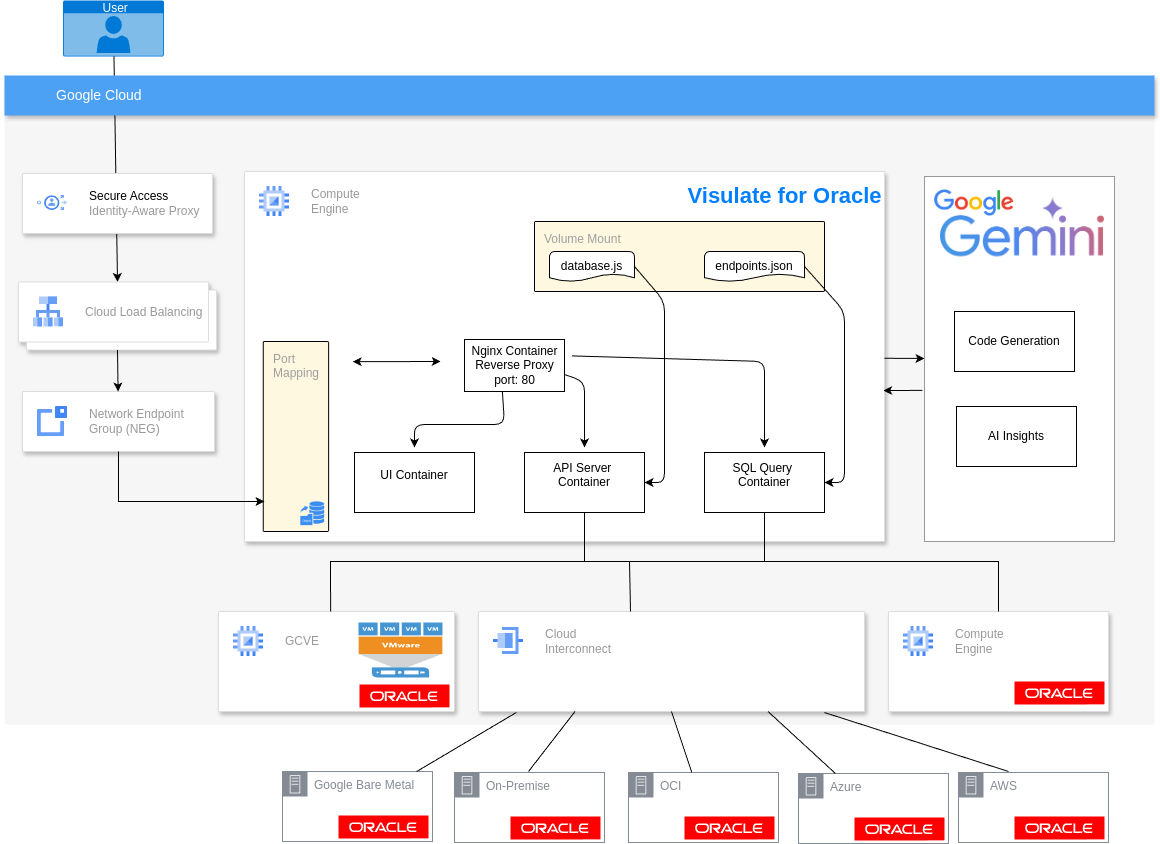
Web users connect to the application via an Nginx reverse proxy container listening on port 80. The connection can be via a load balancer or direct if the VM has been configured with a public IP address. Configuring a load balancer is the recommended approach.
The application components include:
- API Server: A Node.js instance that parses Oracle metadata and orchestrates AI interactions.
- UI: An Angular application served by Nginx.
- SQL Query Engine: A Flask-based service for running ad-hoc queries and generating CSVs.
- AI Agents: A suite of specialized agents (NL2SQL, Schema Analysis, Object Analysis, etc.) running in a Python environment.
- Nginx Proxy: Routes external traffic to the internal UI, API, and SQL services.
The Visulate VM is often provisioned with a private IP address and configured behind an Identity Aware Proxy (IAP) to control access.
Database registration is performed by editing configuration files in an OS directory volume-mounted to the containers.
Copyright © Visulate LLC, 2019, 2025 Privacy Policy