- Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Registered database does not appear in the UI drop down
Follow these steps if the database registration succeeds but some (or all) of your databases are missing.
Call the /endpoints api
The endpoints api lists valid and invalid database connections. Call the api with no arguments to get a list of valid connections. Pass status=invalid as a get parameter to identify invalid ones. Example:
curl https://catalog.visulate.net:3000/endpoints?status=invalid
{"ora18xe":{"connectString":"ap884.visulate.net:91521/XEPDB1","error":"Get connection timed out after 5000 ms"}}
Review the API Server deployment log files
The API Server writes log file entries when the connection fails. These can be accessed from the Deployment details page of the GKE console by selecting the “Container logs” link. They can also be accessed from an api server pod. Use kubectl exec to login to the pod. The log files are located in the /visulate-server/logs directory.
kubectl exec -it {visulate-api-podname} -- bash
bash-4.2# cd logs
bash-4.2# pwd
/visulate-server/logs
bash-4.2# ls
access.log combined.log error.log
head -50 combined.log
Make an API call
The UI calls the /api/ endpoint to get the list of databases to display in the dropdown. Use curl to call it.
Check your browser developer tools for network and console errors
Use the network tab to examine the request to the /api/ endpoint. The response should equal the curl request above. Make sure the Object Filter field in the UI is empty. This is passed as a get parameter to the API. It adds a wildcard filter to the result set which could cause a database to be excluded.
Check the username, password and connect string
Follow the instructions in the network configuration guide to open a bash shell in one of the API server pods. Navigate to the “/visulate-server/config” directory. Use the cat command to view the contents of the “database.js” file.
bash-4.2# cd /visulate-server/config
bash-4.2# cat database.js
This file holds the credentials that the API server reads on startup to establish database connection pools. See the database registration guide for additional details
Test your firewall rules
Follow the steps in the network configuration guide
Check the Visulate account permissions
The visulate account must have been granted CREATE SESSION, SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE and SELECT ANY DICTIONARY. It must not have any additional privileges for security reasons. The API server checks the account’s privileges on startup. It drops the connection if it finds any more or less that the required set. These appear in the API Server log file:
{"level":"info","message":"Creating poolAlias system for db25.visulate.net:401521/XEPDB1",
"timestamp":"2020-05-11T19:40:57.104Z"}
...
{"level":"error","message":"Closing poolAlias system. Account has invalid privileges.
Expected: 'CREATE SESSION,SELECT ANY DICTIONARY,SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE'
Found: 'AQ_ADMINISTRATOR_ROLE,CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW,CREATE TABLE,DBA,DEQUEUE ANY QUEUE,
ENQUEUE ANY QUEUE,GLOBAL QUERY REWRITE,MANAGE ANY QUEUE,SELECT ANY TABLE,UNLIMITED TABLESPACE'",
"timestamp":"2020-05-11T19:41:04.414Z"}
Query Editor is not displayed in the UI
The Query Editor display is controlled by values in the endpoints.json file. If the editor is not being displayed the most likely reason is a missing or misconfigured entry in that file.
The entries in the file must match those of the corresponding database in the database.js file. For example, if the database.js file contains the following endpoint:
{ namespace: 'oracle18XE',
description: '18c XE PDB instance running in a docker container',
connect: { poolAlias: 'oracle18XE',
user: 'visulate',
password: 'HtuUDK%?4JY#]L3:',
connectString: 'db20.visulate.net:41521/XEPDB1',
poolMin: 4,
poolMax: 4,
poolIncrement: 0,
poolPingInterval: 0
}
}
The endpoint.json file must reference the same endpoint and connectString:
{"oracle18XE":"db205.visulate.net:41521/XEPDB1"}
The /endpoints API can be used to get a list of endpoints and connectStrings. The UI calls the /api/{db} API to determine whether to show the query region. The region is shown if a connect string is returned and it matches the connect string returned by the API server for the same database endpoint
AI Chatbot is not displayed in the UI
The GOOGLE_AI_KEY value was not set as an environment variable prior to starting the API server process. Edit the docker-compose.yaml file or kubernetes manifest to set a value.
The UI calls the /ai endpoint to determine whether the AI feature is enabled.
Lost database registration file
Login to an API server pod to view its details - see the username, password and connect string step above.
Google Kubernetes Engine Errors
Pod errors: CrashLoopBackOff
Errors appear on the API Server deployment screen after applying an updated manifest. Example:
CrashLoopBackOff Container 'message-log' keeps crashing.
CrashLoopBackOff Container 'visulate-api' keeps crashing.
What does this mean?
This typically indicates an issue with the database registration file. The deployment container logs may provide additional information. These can be accessed from the Deployment details page. For example, API server will throw an error if there are syntax errors in the registration file. Look for an error like this:
{
"textPayload": "SyntaxError: Unexpected token '{'
at wrapSafe (internal/modules/cjs/loader.js:1054:16)
at Module._compile (internal/modules/cjs/loader.js:1102:27)
at Object.Module._extensions..js (internal/modules/cjs/loader.js:1158:10)
...
}
Deployment updates can also fail if the database registration secret was created with the wrong key. If you don’t see any syntax errors in the log files it could be an issue with the key. The database registration secret key must be database.js. Open the Configuration page in the GKE console for your database registration secret. Examine the key name in the Data section of the page:
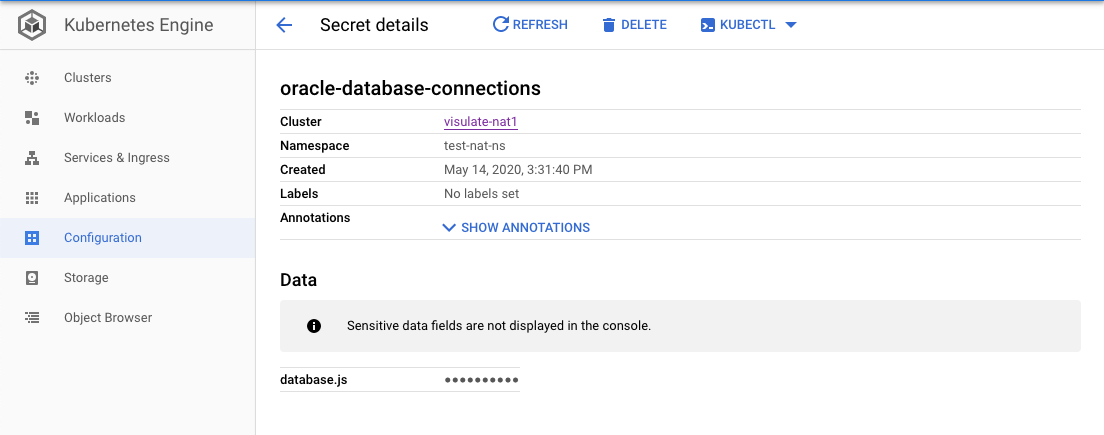
How do I fix it?
Follow the validation instructions in the database registration guide to check for errors. Create a new secret with the updated file then update the API Server deployment.
Pod unschedulable
The rolling update to a new configuration hangs. The old pods are still active and new ones are not created.
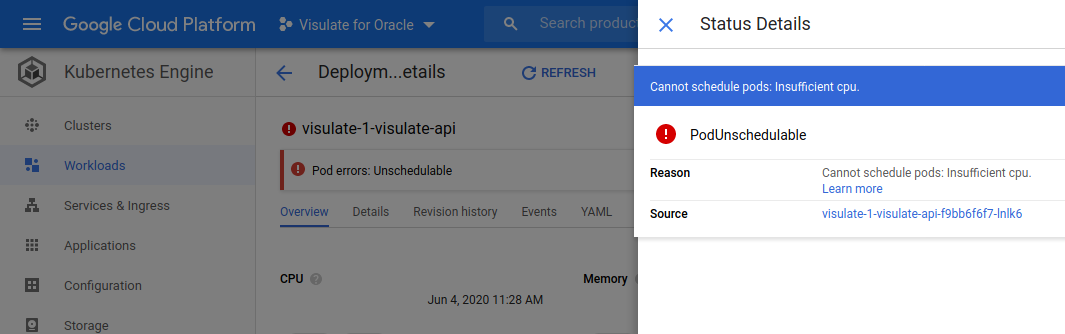
What does this mean?
There are insufficient resources in the cluster. See GKE troubleshooting guide.
How do I fix it?
Add resources to the cluster or reduce the number of API Server replicas.
kubectl apply fails with Conflict
kubectl returns an error when attempting to update the database registration file secret. Example:
$ kubectl apply -f ../dev-files/deployment.yaml
Error from server (Conflict): error when applying patch:
{ "metadata":{"annotations":{"deployment.kubernetes.io/revision"
...
:"Progressing"}],"observedGeneration":1,"replicas":1}}
to:
Resource: "extensions/v1beta1, Resource=deployments",
GroupVersionKind: "extensions/v1beta1, Kind=Deployment"
Name: "visulate-1-visulate-api", Namespace: "default"
for: "../dev-files/deployment.yaml":
Operation cannot be fulfilled on deployments.extensions "visulate-1-visulate-api":
the object has been modified; please apply your changes to the latest version and try again
What does this mean?
The deployment configuration has changed since the manifest was created.
How do I fix it?
Follow the instructions in the database registration guide to generate a new one.
Copyright © Visulate LLC, 2019, 2025 Privacy Policy