Analyzing PL/SQL
Visulate for Oracle generates documentation for every object in an Oracle database including all PL/SQL packages, procedures and package bodies. The object selection menu can be used to identify every PL/SQL object in a schema.
Review the structure of a PL/SQL object
Selecting an object opens a report showing its source code
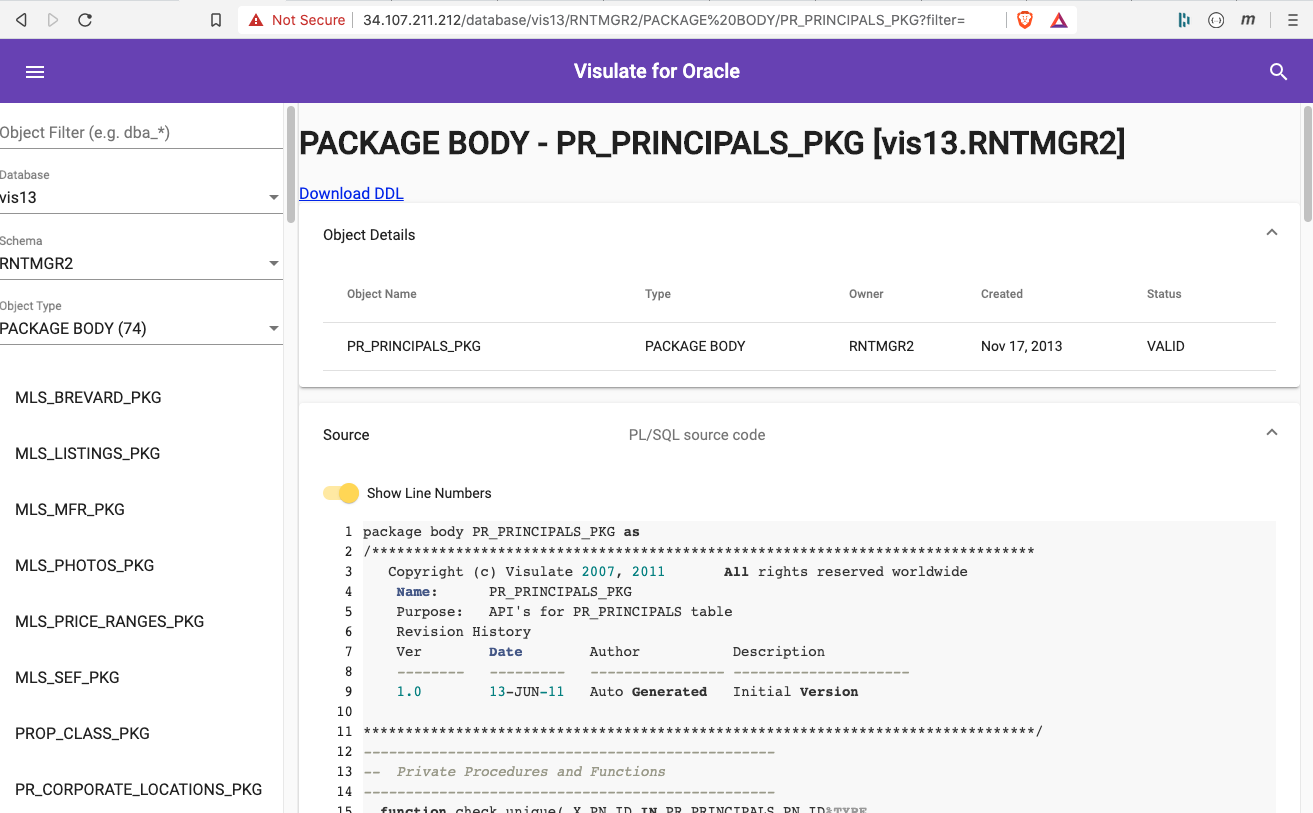
It also extracts SQL statements and lists dependencies.
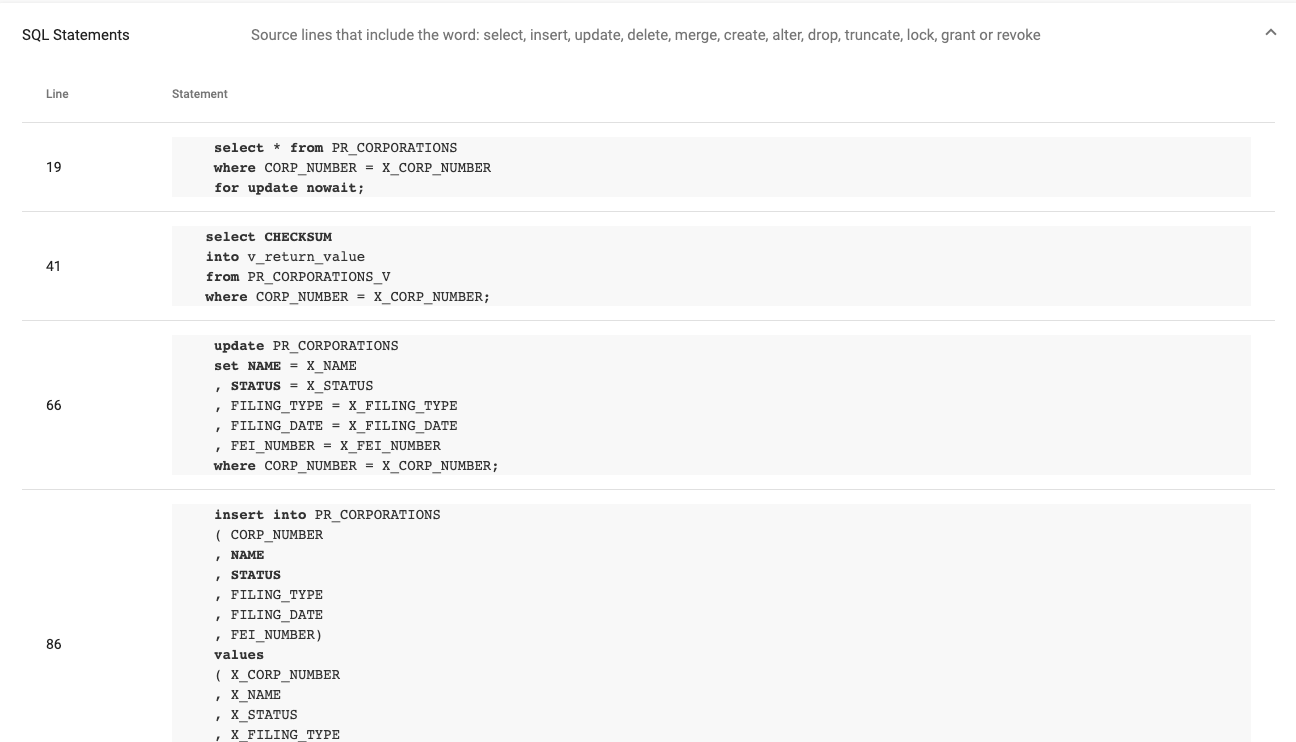
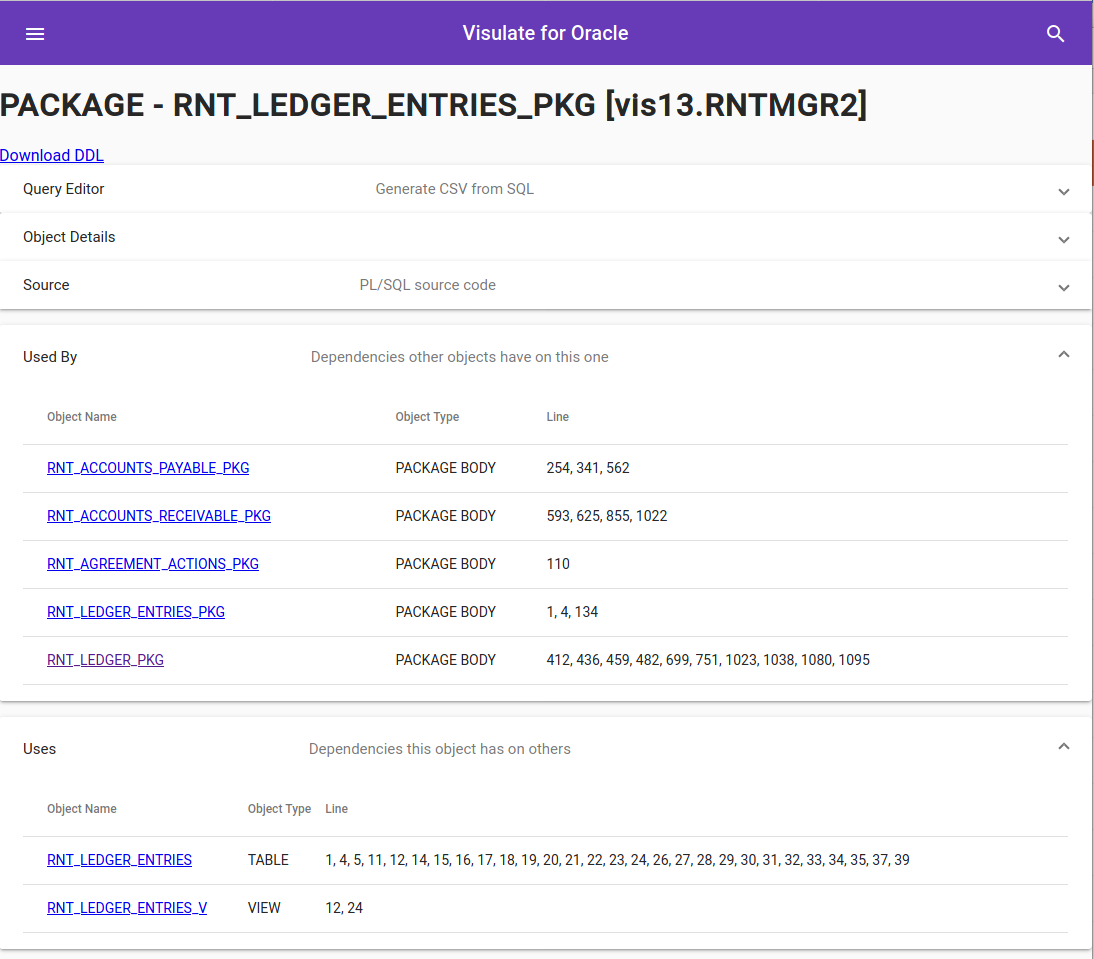
Each dependency appears as a link to the corresponding object and includes a reference to the line number in the source code where the dependency appears.
AI Chat
Visulate’s generative AI features can be used to analyze PL/SQL packages and package bodies. The following example shows a couple of questions for a stored procedure and the AI’s response:
You:
what is this
Visulate:
This is a PL/SQL package called RNT_ACCOUNTS_RECEIVABLE_PKG owned by user RNTMGR2. It was created on October 24, 2021 and is currently valid. It contains a number of procedures and functions for interacting with the RNT_ACCOUNTS_RECEIVABLE table. These procedures and functions are used for performing various operations on accounts receivable records, such as:
- Inserting new accounts receivable records: The insert_row and insert_row2 procedures allow you to create new accounts receivable records in the database.
- Updating existing accounts receivable records: The update_row, update_row_amount, and update_row2 procedures allow you to modify existing records in the database.
- Deleting accounts receivable records: The delete_row and delete_row2 procedures allow you to remove records from the database.
- Generating a checksum: The get_checksum function calculates a checksum for a given accounts receivable record. This can be used to validate that the record has not been modified by another user.
- Generating a payments list: The generate_payments_list procedure generates a list of payments that are due for a particular business unit. It takes into account the effective date and whether late fees should be generated.
- Deleting payments from a list: The delete_payments_list_from procedure deletes all payments from the list that are due on or after a specified date.
- Setting up a payments list: The setup_payments_list procedure sets up a list of payments for a particular business unit between a specified start date and end date.
- Updating payment details from allocations: The update_payment_from_allocation procedure updates the payment details for a given account receivable record based on payment allocations.
- Getting the maximum allocation amount for an agreement action: The get_max_alloc_for_agr_action function returns the maximum amount that has been allocated to a particular agreement action.
- Deleting accounts receivable records for a given agreement action: The DELETE_AGR_ACTION_RECEIVABLE procedure deletes all accounts receivable records that are associated with a particular agreement action.
- Updating payment details: The update_alloc procedure updates the payment details for a given payment allocation.
- Deleting payment allocation records: The delete_receivable_row procedure deletes a specific payment allocation record.
- Other miscellaneous functions: The package also contains a number of other functions, such as PAYMENT_TYPE_UTILITES, PAYMENT_TYPE_TAX, and PAYMENT_TYPE_INSURANCE, which return constant values representing different payment types.
The package code also includes comments that provide further information about the purpose and functionality of each procedure and function. This is a critical part of the package because it helps developers to understand how to use the package and to maintain it over time.
Would you like to know more about this package or any of the procedures or functions it contains?
You:
write a python module to call this package
Visulate:
import cx_Oracle
def connect_to_database(username, password, host, port, service_name):
"""Connects to the Oracle database.
Args:
username (str): The username for the database.
password (str): The password for the database.
host (str): The hostname of the database server.
port (int): The port number of the database server.
service_name (str): The service name of the database.
Returns:
cx_Oracle.Connection: A connection object to the database.
"""
dsn = cx_Oracle.makedsn(host, port, service_name=service_name)
connection = cx_Oracle.connect(username, password, dsn)
return connection
def execute_procedure(connection, package_name, procedure_name, *args):
"""Executes a procedure in the specified package.
Args:
connection (cx_Oracle.Connection): The connection object to the database.
package_name (str): The name of the package.
procedure_name (str): The name of the procedure.
*args: The arguments to pass to the procedure.
Returns:
None
"""
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.callproc(f"{package_name}.{procedure_name}", args)
cursor.close()
def execute_function(connection, package_name, function_name, *args):
"""Executes a function in the specified package.
Args:
connection (cx_Oracle.Connection): The connection object to the database.
package_name (str): The name of the package.
function_name (str): The name of the function.
*args: The arguments to pass to the function.
Returns:
The return value of the function.
"""
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(f"BEGIN :result := {package_name}.{function_name}(:args); END;",
{'result': cx_Oracle.NUMBER, 'args': args})
result = cursor.var(0).getvalue()
cursor.close()
return result
# Example usage:
# Database connection details
username = "username"
password = "password"
host = "hostname"
port = 1521
service_name = "service_name"
# Connect to the database
connection = connect_to_database(username, password, host, port, service_name)
# Execute a procedure
execute_procedure(connection, "RNT_ACCOUNTS_RECEIVABLE_PKG", "update_row", 1, "2023-12-31", 1000, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, "Y", "checksum", 1, 1)
# Execute a function
result = execute_function(connection, "RNT_ACCOUNTS_RECEIVABLE_PKG", "get_checksum", 1)
# Print the result
print(f"Checksum: {result}")
# Close the database connection
connection.close()
This module defines three functions:
- connect_to_database: Connects to the Oracle database using the provided credentials and connection details.
- execute_procedure: Executes a PL/SQL procedure in the specified package.
- execute_function: Executes a PL/SQL function in the specified package and returns the function’s result.
The example usage demonstrates how to connect to the database, execute a procedure, and execute a function.
Remember to replace the placeholder values with your actual database connection details.
Identify package differences in 2 databases
The Download DDL link in the menu can be used to generate a file with DDL for the listed objects.
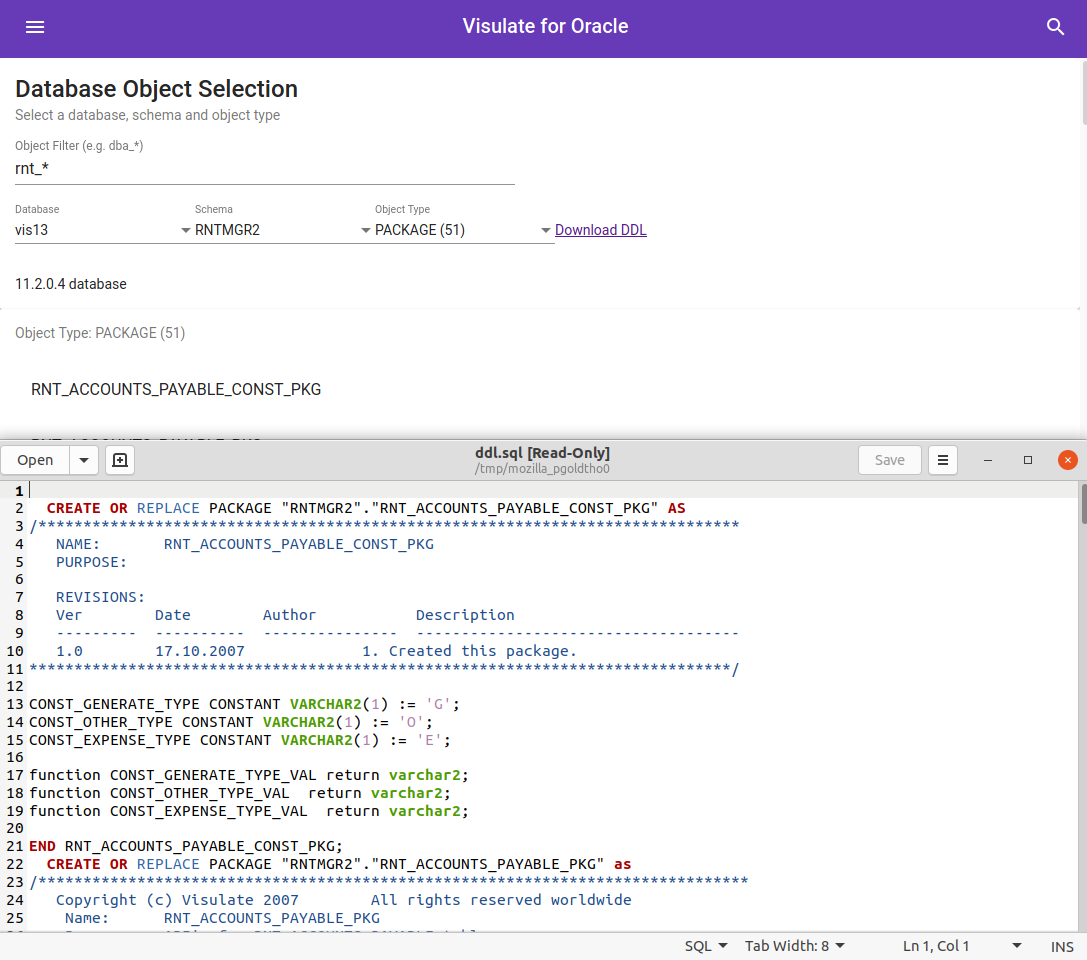
This can be used to identify differences between packages, procedures or package bodies in different databases. Simply generate the file for each database and then diff them.
Copyright © Visulate LLC, 2019, 2025 Privacy Policy