- Analyzing Oracle database complexity
Analyzing Oracle database complexity
The first step in an Oracle database migration is to analyze the source database’s complexity. Much of the information required to do this can be obtained by querying the Oracle data dictionary. The Oracle database dictionary is a set of system catalog views which contain metadata about the database. This metadata includes the number and type of different schema objects used, the source code for stored procedures, the server configuration and more.
Visulate for Oracle includes a series of predefined database analysis queries. They run automatically when the database or schema selection changes in the UI.
Database Analysis
Select a database on the homepage of the application to run the database analysis queries
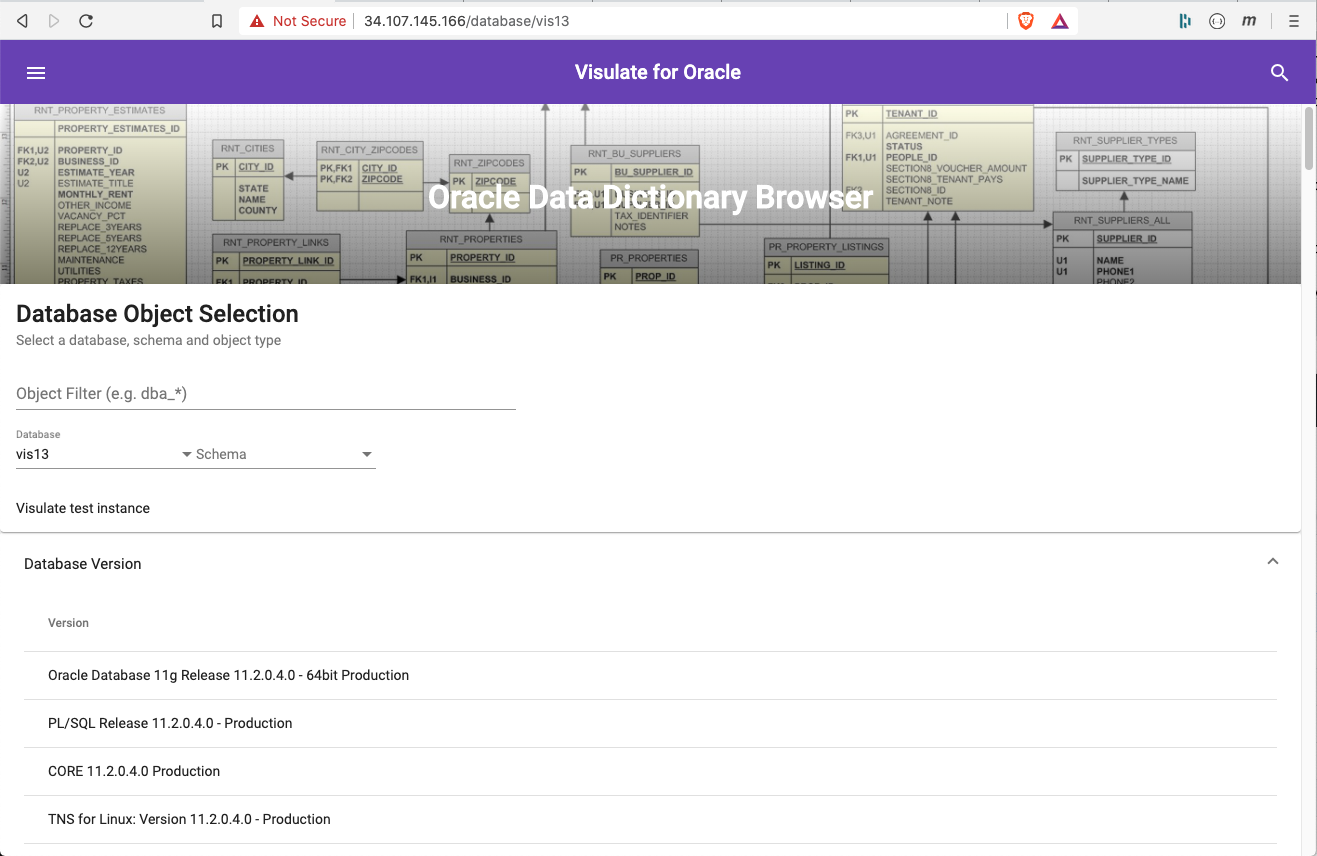
This will run the following queries:
Database Version
List the database version
select banner as "Version" from v$version
Oracle Cloud Autonomous Database Instance
Is the database running on Oracle Cloud infrastructure?
select decode( count(*), 0, 'No',
'Yes') as "Autonomous Database"
from dba_objects
where object_name = 'DBMS_CLOUD'
E-Business Suite Schema Detected
Is it an E-Business suite instance?
select decode(count(*), 1, 'Yes',
'No') as "EBS Schema"
from dba_tables
where owner='APPLSYS'
and table_name = 'FND_APPLICATION'
Patch History
What patches have been applied to this instance?
select to_char(action_time, 'Mon dd, yyyy hh24:mi') as "Time"
, action as "Action"
, namespace as "Namespace"
, version as "Version"
, id as "ID"
, comments as "Comments"
from sys.REGISTRY$HISTORY
order by action_time
Database Links
List database links
select owner as "Schema",
db_link as "Database Link",
username as "Username",
host as "Connect String"
from dba_db_links
order by 1, 2
Invalid Objects
Count invalid objects by schema
select owner as "Owner"
, object_type as "Object Type"
, count(*) as "Count"
from dba_objects
where status = 'INVALID'
group by owner, object_type
order by owner, object_type
SGA Size
List the total size of the system global area
select round(sum(value/1024/1024/1024), 2)as "Total Size (GB)"
from v$sga
SGA Free
List the total free space
select round(sum(bytes/1024/1024), 2) as "Free Memory (MB)"
from v$sgastat
where name like '%free memory%'
Database Size
List the size of each tablespace
select nvl(tablespace_name, 'Total') as "Tablespace",
round(sum(bytes)/1024/1024/1024, 2) as "Size (GB)"
from dba_data_files
group by grouping sets((), (tablespace_name))
order by 2 desc
Space Used
List the storage allocation for each schema
select nvl(owner, 'Total') as "Schema",
round(sum(bytes)/1024/1024/1024, 2) as "Size (GB)"
from dba_segments
group by grouping sets((), (owner))
order by 2 desc
System Utilization Statistics
Display system utilization statistics from the operating system
select comments as "Statistic"
, value
, to_char(value, 'FM999,999,999,999') as "Value"
from v$osstat
Database Feature Usage
Displays database feature usage statistics
select f.name as "Feature"
, f.detected_usages as "Times Used"
, to_char(f.first_usage_date, 'Mon DD, YYYY') as "First Used"
, to_char(f.last_usage_date, 'Mon DD, YYYY') as "Last Used"
, f.currently_used as "Used Now"
from dba_feature_usage_statistics f
, v$database d
where f.detected_usages > 0
and d.dbid = f.dbid
order by f.name
Schema Analysis
Select a database user from the schema drop down to run schema reports.
Schema Status
List the account status (e.g. open, locked or expired) along with the default tablespaces for the schema.
select account_status as "Status"
, default_tablespace as "Default Tablespace"
, temporary_tablespace as "Temporary Tablespace"
from dba_users
where username = :owner
Data Types
Count the column data type usage in the schema’s tables and views. Look for Oracle specific data types if you are planning to migrate from Oracle to Postgres or MySQL.
select data_type as "Data Type"
, count(*) as "Count"
from dba_tab_columns
where owner = :owner
group by data_type
order by data_type
Spatial
List and link to tables and views with spatial columns
select c.table_name as "Object Name"
, o.object_type as "Type"
, c.column_name as "Column"
from dba_tab_columns c
, dba_objects o
where c.owner = :owner
and c.data_type= 'SDO_GEOMETRY'
and o.owner = c.owner
and o.object_name = c.table_name
order by c.table_name, o.object_type, c.column_name
Non Standard Indexes
List non standard indexes
select index_type as "Type"
, index_name as "Index"
from dba_indexes
where owner = :owner
and index_name like :object_name ESCAPE :esc
and index_type not in ('NORMAL', 'LOB')
order by index_name, index_type
PL/SQL Analysis
Visulate for Oracle generates documentation for every object in an Oracle database including all PL/SQL packages, procedures and package bodies.
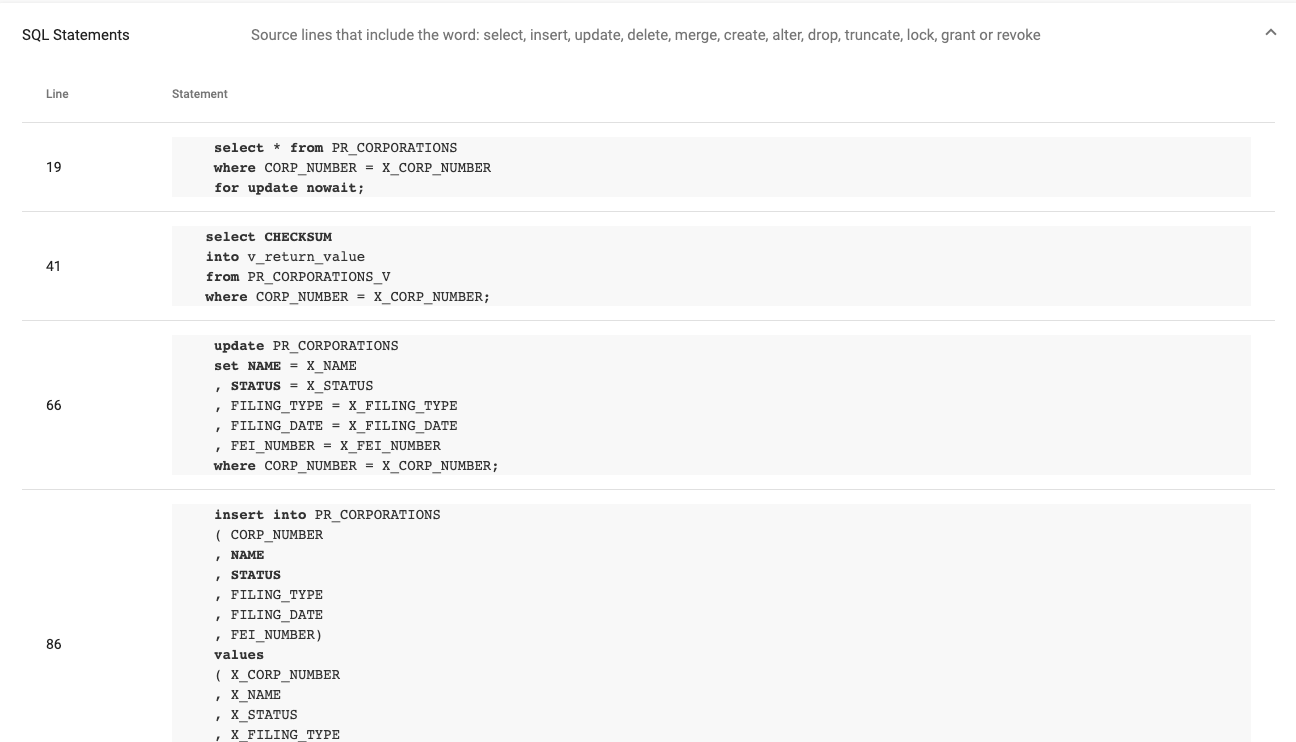
Review the structure of a PL/SQL object
Selecting an object opens a report showing its source code, extracted SQL statements, and dependencies. Each dependency includes a reference to the line number in the source code where the dependency appears.
Analyzing PL/SQL with AI
You can use the AI chatbot to explain business logic, generate test cases, or translate PL/SQL into other languages like Python.
- Explain Logic: Ask “Summarize the logic in this package.”
- Code Conversion: Ask “Convert this procedure into a Python function using cx_Oracle.”
Dependency Analysis
Every Oracle database maintains a record of the dependencies between its objects in the SYS.DEPENDENCY$ table. Visulate for Oracle identifies these dependencies to help you understand the impact of changes or plan partial migrations.
Using the UI
Dependency reports are included at the bottom of each database object report.

AI Powered Dependency Analysis
Ask the AI agent to identify complex relationships: “Analyze the downstream dependencies of the ‘ORDERS’ table” or “Show me all objects that would be invalidated if I modified this view.”
Object Collection API
The object collection API is used to identify a collection of objects along with the dependent objects that are needed to create them. It is designed to support partial schema migrations.
curl -L 'https://my-domain.com/api/collection/my-db' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '[{"owner": "HR", "type": "PACKAGE", "name": "EMP_MGMT_PKG", "status": "*"}]'
API Access
The database and schema analysis reports can be initiated via API calls
Database analysis
Call the /api endpoint passing the registered database as a path parameter /api/{database} to run the database reports. Example:
curl -X GET "https://my-domain.com/api/my-db" -H "accept: application/json" | json_pp
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 9354 100 9354 0 0 10653 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 10641
[
{
"description" : "",
"display" : [
"Version"
],
"rows" : [
{
"Version" : "Oracle Database 11g Release 11.2.0.4.0 - 64bit Production"
},
{
"Version" : "PL/SQL Release 11.2.0.4.0 - Production"
},
... etc
Schema analysis
Call the /api endpoint passing the registered database and schema as path parameters /api/{database}/{schema} to run the schema reports. Note the schema name is case sensitive. Example:
curl -X GET "https://my-domain.com/api/my-db/MY-SCHEMA" -H "accept: application/json"| json+pp
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 1621 100 1621 0 0 2315 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 2312
[
{
"description" : "",
"display" : [
"Status",
"Default Tablespace",
"Temporary Tablespace"
],
"rows" : [
{
"Default Tablespace" : "RNT_DATA2",
"Status" : "OPEN",
"Temporary Tablespace" : "TEMP"
}
],
"title" : "Schema Status"
},
... etc
Copyright © Visulate LLC, 2019, 2025 Privacy Policy