Install a TLS Certificate
Visulate for Oracle creates a temporary TLS certificate for the application. You need to replace this if you want to support https requests.
Replacing the temporary cert with a self signed certificate
Generate a private key:
openssl genrsa -out visulate.key 2048
Create a certificate signing request:
openssl req -new -key visulate.key -out visulate.csr \
-subj "/CN=your-domain"
Where “your-domain” is a domain name where you want to host the application. For example, you want the load balancer to serve requests from the visulate.mycorp.com domain. Your certificate signing request would look like this:
openssl req -new -key visulate.key -out visulate.csr \
-subj "/CN=visulate.mycorp.com"
Create a certificate:
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in visulate.csr -signkey visulate.key \
-out visulate.crt
Create a secret to hold the certificate:
kubectl create secret tls visulate-tls --cert visulate.crt --key visulate.key --namespace=test-ns
Find the Ingress name:
kubectl get ingress --namespace=test-ns
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
visulate-for-oracle-01-igs * 34.107.211.212 80, 443 22h
Download the Ingress manifest:
kubectl get ingress visulate-for-oracle-01-igs --namespace=test-ns -oyaml > ingress.yaml
Edit the downloaded manifest file (ingress.yaml) and update the tls secretName to “visulate-tls” (or whatever you called your tls secret):
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
...
- backend:
serviceName: visulate-for-oracle-01-visulate-ui-svc
servicePort: 80
path: /database/*
tls:
- secretName: visulate-tls
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- ip: 34.107.211.212
Validate the edited manifest:
kubectl apply --dry-run --validate --namespace=test-ns -f ingress.yaml
Update the Ingress:
kubectl apply --namespace=test-ns -f ingress.yaml
Describe your ingress. Examine the TLS entry. It should read “visulate-tls terminates”
$ kubectl describe ingress visulate-for-oracle-01-igs --namespace=test-ns
Name: visulate-for-oracle-01-igs
Namespace: test-nat-ns
Address: 34.107.211.212
Default backend: visulate-for-oracle-01-visulate-ui-svc:80 (10.8.1.74:80)
TLS:
visulate-tls terminates
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
...
Wait about 5 minutes for the load-balancer configuration to complete then test. Example:
curl -v https://visulate.mycorp.com
Using a Google managed certificate
Find the Ingress IP address:
$ kubectl get ingress visulate-for-oracle-01-igs --namespace=test-ns
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
visulate-for-oracle-01-igs * 34.107.211.212 80 23h
Create a DNS record for your domain entry which resolves to this address.
Create a managed certificate manifest file:
---
apiVersion: networking.gke.io/v1
kind: ManagedCertificate
metadata:
name: visulate-certificate
spec:
domains:
- visulate.mycorp.com
Apply the file to your cluster:
kubectl apply -f managed-cert.yaml --namespace=test-ns
Add a “networking.gke.io/managed-certificates” annotation to your ingress:
kubectl annotate ingress visulate-for-oracle-01-igs --namespace=test-nat-ns \
--overwrite networking.gke.io/managed-certificates=visulate-certificate
This will trigger an update to the load balancer associated with the ingress. You can monitor its progress from the Network Services -> Load balancing screen. Click on the Frontend HTTPS Certificate entry for the managed cert. Note: there may be more than one certificate associated with the load balancer.
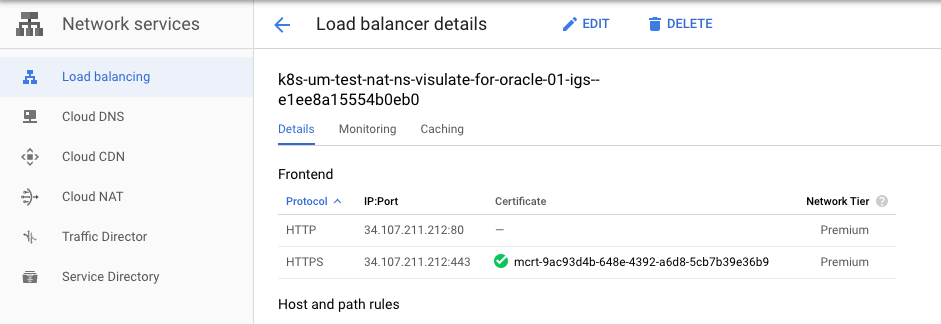
Wait for the status to change from “PROVISIONING” to “ACTIVE”
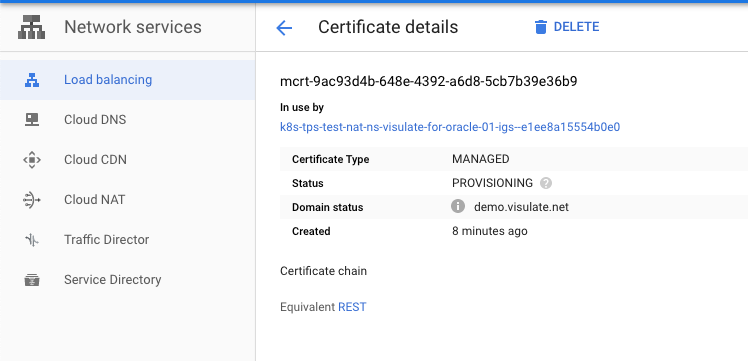
You can remove the temporary TLS cert from the ingress after the Google managed cert becomes active.
Download the Ingress manifest:
kubectl get ingress visulate-for-oracle-01-igs --namespace=test-ns -oyaml > ingress.yaml
Edit the file (ingress.yaml) and remove TLS entry:
tls:
- secretName: visulate-for-oracle-01-tls
Validate the edited manifest:
kubectl apply --dry-run --validate --namespace=test-ns -f ingress.yaml
Update the Ingress:
kubectl apply --namespace=test-ns -f ingress.yaml
Wait about 5 minutes for the load-balancer reconfiguration to complete then test. Example:
curl -v https://visulate.mycorp.com
Copyright © Visulate LLC, 2019, 2025 Privacy Policy